Diagnosing Localized and Distributed Bearing Faults by Bearing Noise Signal Using Machine Learning and Kurstogram
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31357/ait.v2i2.5475Abstract
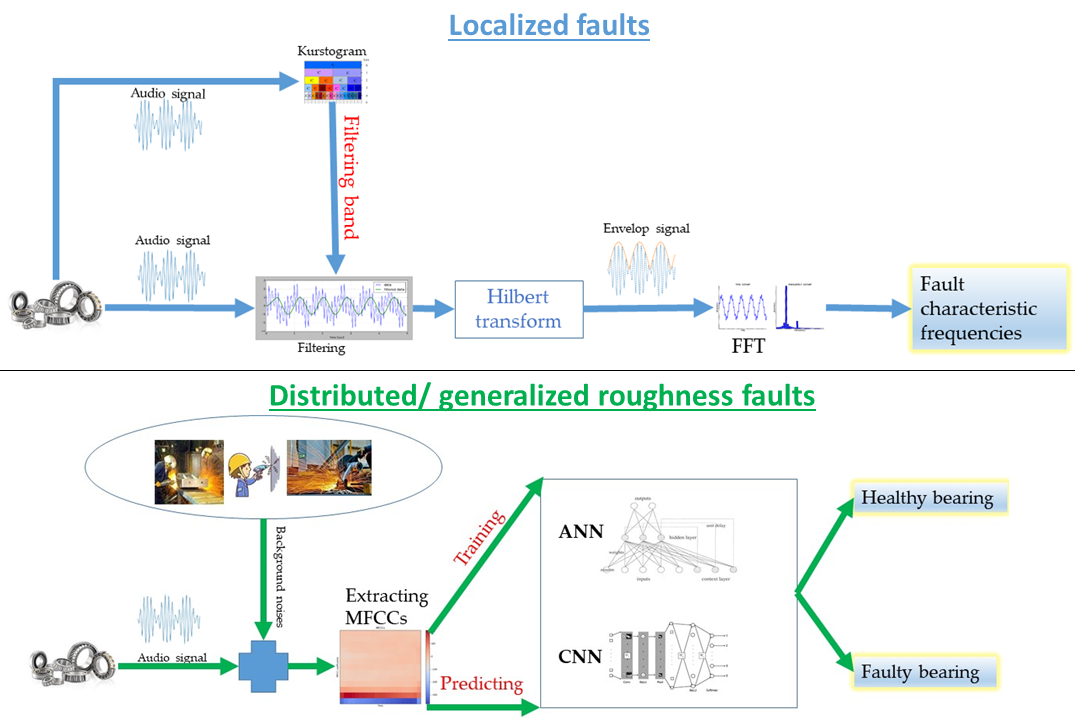
Bearings are a common component and crucial to most rotating machinery. Their failures are the causes for more than half of the total machine failures, each with the potential to cause extreme damage, injury, and downtime. Therefore, fault detection through condition monitoring has a significant importance. Since the initial cost of standard condition monitoring techniques such as vibration signature analysis is high and has a long payback period, the condition monitoring via audio signal processing is proposed for both localized faults and distributed/ generalized roughness faults in the rolling bearing. It is not appropriate to analyze bearing faults using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of the noise signal of bearing since localized faults are Amplitude Modulated (AM) and mixed up with background noises. Localized faults are processed using Kurstogram technique for finding the appropriate filtering band because localized faulty bearings produce impulsive signals
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Kanagasundram Jathursajan, Akila Wijethunge

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Authors hold the copyright of their manuscripts, and all articles are circulated under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, as long as that the original work is properly cited.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. The authors are responsible for securing any permissions needed for the reuse of copyrighted materials included in the manuscript.




