Design and Simulation of a Novel Magnetic Microactuator for Microrobots in Lab-On-a-Chip Applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31357/ait.v2i3.5521Keywords:
microactuator, magnetic, microrobotics, lab-on-a-chipAbstract
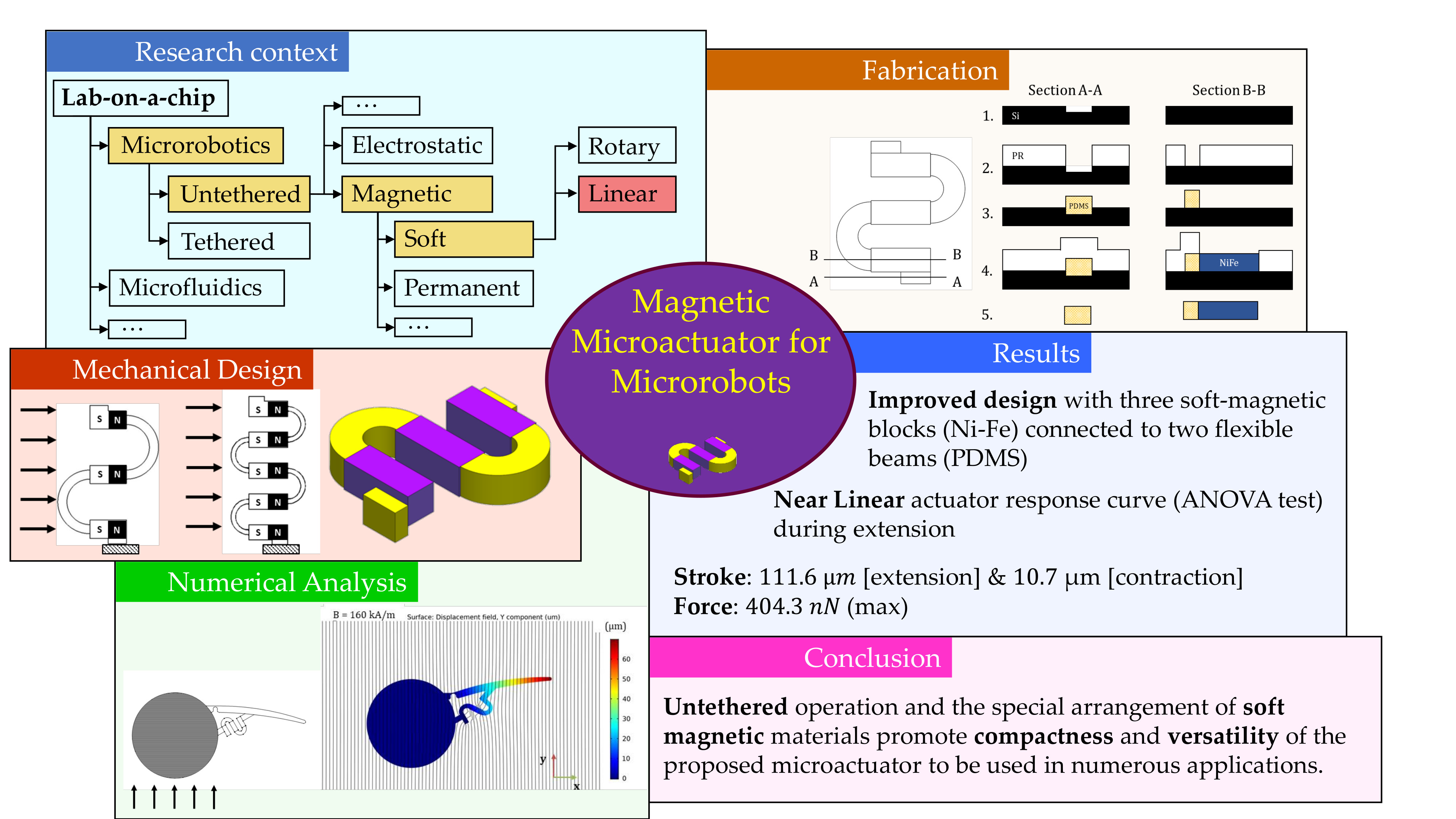
This article presents the design of a magnetic microactuator comprising soft magnetic material blocks and flexible beams. The modular layout of the proposed microactuator promotes scalability towards different microrobotic applications using low magnetic fields. The presented microactuator consists of three soft magnetic material (Ni-Fe 4750) blocks connected together via two Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) semi-circular beams. A detailed design approach is highlighted giving considerations toward compactness, range of motion and force characteristics of the actuator. The actuator displacement and force characteristics are approximately linear in the magnetic field strength range of 80-160 kA/m. It can achieve maximum displacements of 111.6 µm (at 160 kA/m) during extension and 10.7 µm (at 80 kA/m) during contraction under no-load condition. The maximum force output of the microactuator, computed through a contact simulation, was 404.3 nN at a magnetic field strength of 160 kA/m. The microactuator achieved stroke angles up to 18.4 in a study where the microactuator was integrated with a swimming microrobot executing rowing motion using an artificial appendage, providing insight into the capabilities of actuating untethered microrobots.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Nisal Minula Perera Kankanige, Gihan Charith Premachandra Hanchapola Appuhamilage, Shanuka Kamesh Dodampegama, Ranjith Amarasinghe Yattowita Withanage

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Authors hold the copyright of their manuscripts, and all articles are circulated under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, as long as that the original work is properly cited.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. The authors are responsible for securing any permissions needed for the reuse of copyrighted materials included in the manuscript.




