The Importance of Involving Community Organizations for Preventing Destructive Fishing Activities in Mannar, Sri Lanka
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31357/ait.v1i1.4850Abstract
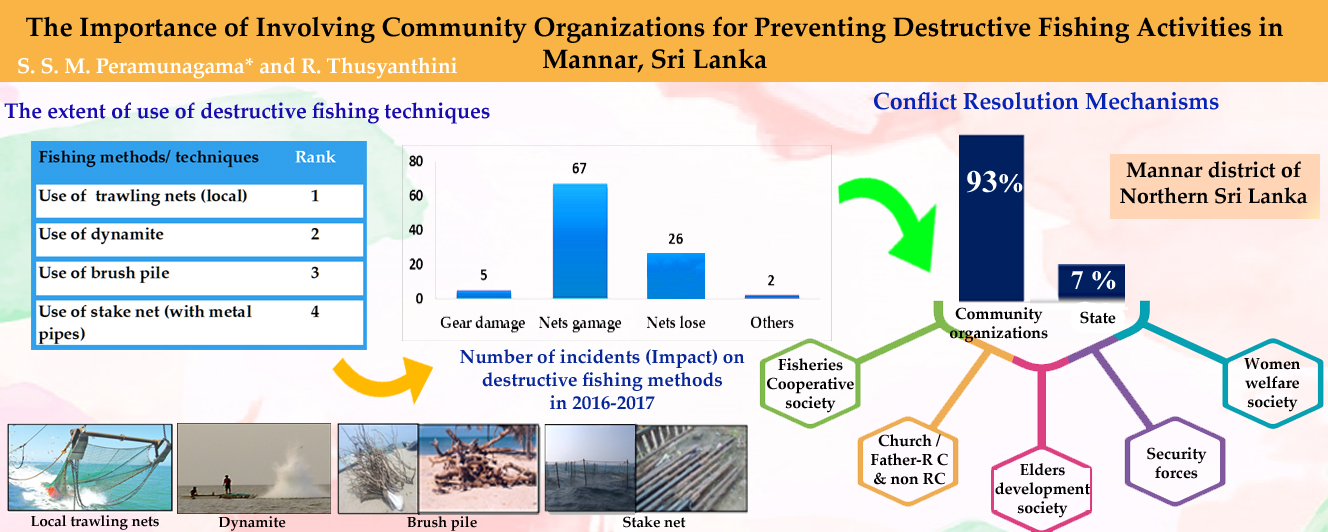
The irresponsible destructive fishing practices with respect to the ecosystem approach have remained a major concern since the elimination of these practices has not been easy despite efforts. There is an urgent need to identify the different types of destructive fishing methods and their threats to fisheries then, to assess how the different organizations/groups/individuals confront with these threats. This study was carried out in Pesalai, a fisheries village in the Mannar district of Northern Sri Lanka in the years 2016 and 2017. The methodology employed consists of a pre-tested structured questionnaire in the field survey with a random sample of 310 fishers and a focus group discussion was conducted where 20 fishers actively participated. The results revealed that trawling net fishing, dynamite fishing, brush pile fishing, and stake net were being used extensively by the fishers. However, the use of such gears have facilitated to catch more fish and earning a high income. Resultant, the major negative impacts were gearing damages, nets damages and net loss. It is apparently found that, the majority of fisheries (93%) had faith in fisher community organizations (fisheries co-op society, the church/father and women welfare society) in terms of resolving conflicts which were raised by destructive fisheries (wrangling, argument and dissension) while 7% of the respondents have faith in the state to resolve conflicts. The fisheries believed that, the government supports for fishing activities was not well required. Hence, it is strongly concluded that the Regulations should be enforced, as a joint effort between the department of fisheries and community organizations.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2021 S. S. M. Peramunagama, Thusyanthini Ramanathan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Authors hold the copyright of their manuscripts, and all articles are circulated under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, as long as that the original work is properly cited.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. The authors are responsible for securing any permissions needed for the reuse of copyrighted materials included in the manuscript.




