Recent Advancements in Chitosan-based Adsorbents for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Media
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31357/vjs.v1is1.6710Abstract
Contamination of aqueous environments by Cr(VI) has become a matter of concern owing to its detrimental impacts on human health with its long-term exposure. Thus, effective treatment of adulterated aqueous media is critical in terms of the health and safety of humans together with flora and fauna. Currently, chitosan is considered an excellent adsorptive material for the
remediation of Cr(VI) contamination owing primarily to its biodegradability, non-toxicity, abundance, and ability to modify its microstructure. The present review focuses on the up-to-date progression of chitosan-based sorbents that can be utilized in the mitigation of Cr(VI) oxyanions from aqueous media. This paper provides an overview of pristine chitosan along with recent
advancements and insights into structurally and chemically modified chitosan. Chitosan has been chemically modified through cross-linking, grafting, and/or combination with other adsorptive materials to enhance its performance in Cr(VI) removal. Structurally modified chitosan-based hybrid materials that are commonly used in Cr(VI) removal include magnetic adsorbents,
hydrogels, aerogels, and nano/microparticles. The sorption capacities of chitosan-based hybrid materials have varied from 27.25 - 357.14 mg g-1 depending on the type of adsorbent, dosage, initial Cr(VI) concentration, pH, and type of modification. Also, beneficial information through a compare-and-contrast of the effectiveness of the stated sorbent materials and their variants in the
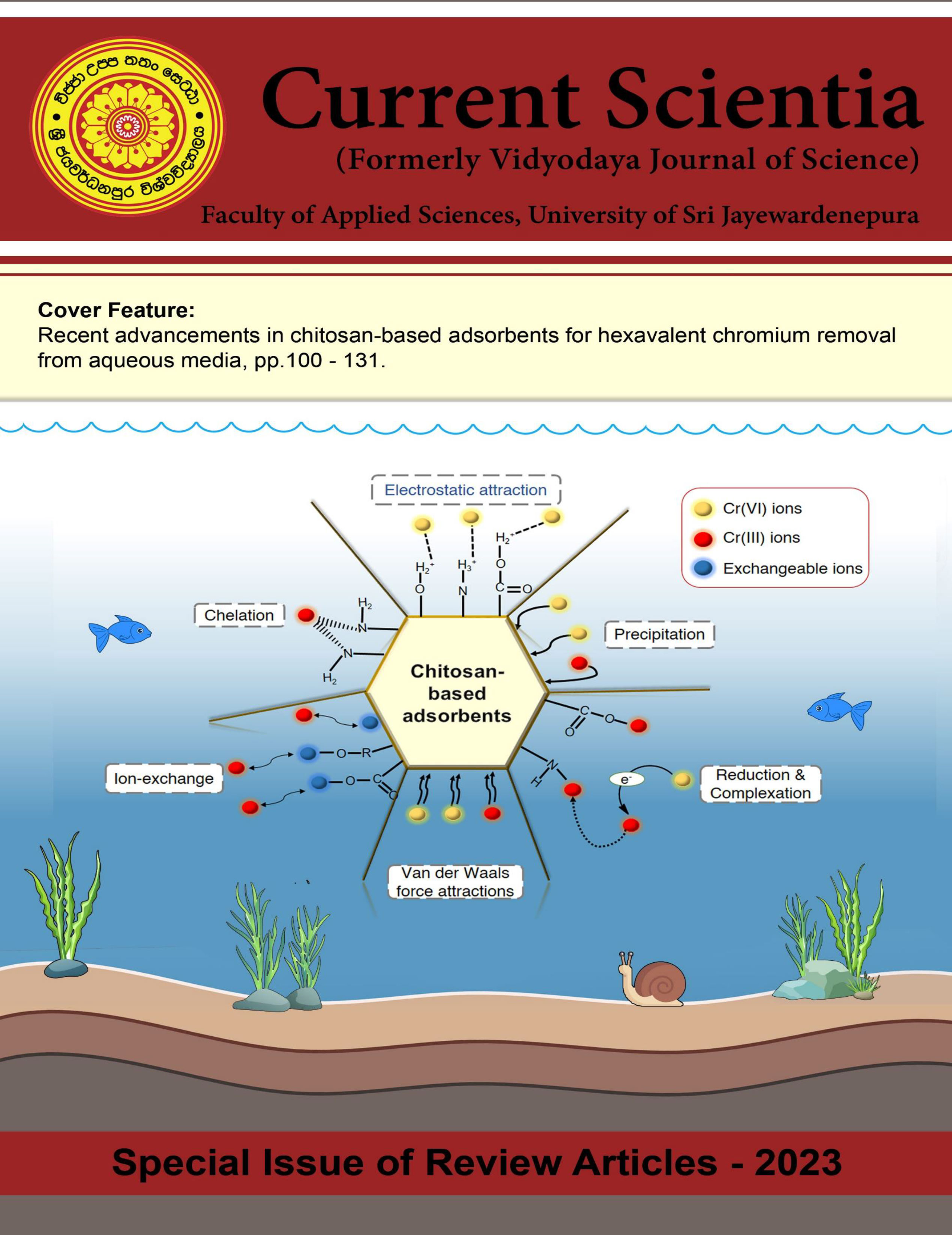
mitigation of Cr(VI) is provided. Furthermore, mechanisms of Cr(VI) removal by chitosan-based sorbents accentuating the main governing mechanism, electrostatic interactions are described and discussed. Desorption and regeneration studies are presented to assess the reusability of the chitosan-based adsorptive materials utilized in the mitigation of Cr(VI) contamination. Desorption
studies reveal that sorption of Cr(VI) onto most of the chitosan-based adsorbents are fairly reversible with desorbed percentages above 60% with the usage of an efficient stripping agent. Through the literature survey of approximately 100 recently published papers, it could be evinced that chitosan-based adsorbents have proved to be an outstanding sorbent even if some challenges
remain.
Keywords: Adsorption, chitosan, Cr(VI), hybrid materials, mechanism