Building Integrated Vegetation Systems and their Sustainability Aspects; A Literature Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31357/vjs.v26i01.6407Abstract
Abstract:
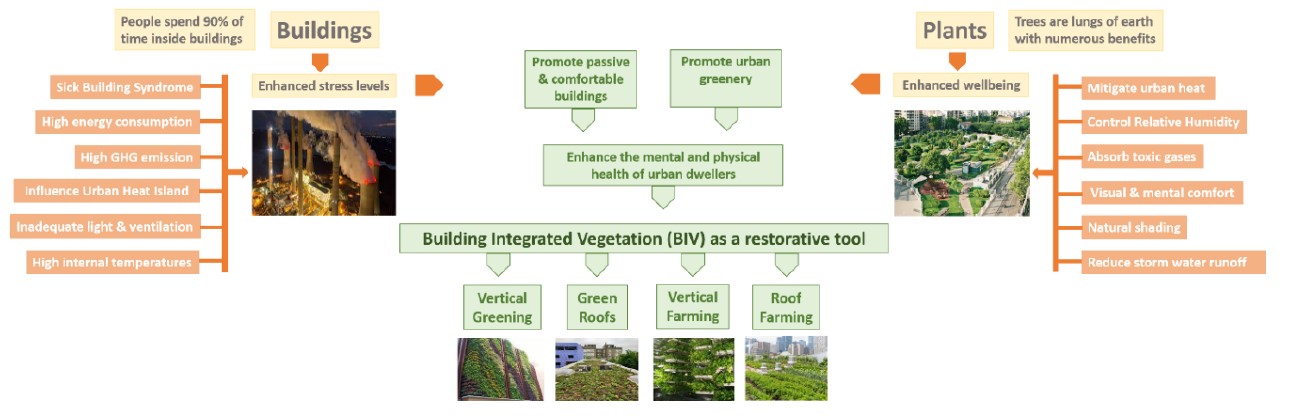
There is a growing need of sustainable building development all over the world. It aims to decrease the adverse effects to the environment due to urbanization and escalating population growth. Since the building construction is considered as one of the main concerns, the priority was given to mitigate the negative impact to the environment. Therefore, incorporating sustainable elements and techniques to the buildings to regain the land loss due to construction activities in cities is currently practicing. Adding various vegetation types through different approaches, to obtain the expected results of better living condition around the building is called as building integrated vegetation systems (BIV). Vertical gardening systems, vertical farms, constructed green roofs and roof farms can be stated as main categories of BIV systems. However, there is a paucity of published critical reviews on such systems and therefore, this study is an attempt to review the overall sustainability aspects of BIV systems including environmental sustainability, economic sustainability and social sustainability. This study consists with a critical review of 114 research publications from relevant journals and online scientific databases. Finally, the identified sustainability aspects of each BIV systems were analyzed to select the best option in terms of greening a building which can be recommended for the implementations in future. Mainly, the importance of moving towards the sustainable solution which meets the food needs through BIV is finally discussed. Finally, it can be concluded that by incorporating green architecture with smart agriculture, we can expect green, healthy and productive cities which fulfill the main requirements of sustainable cities. Though there are many challenges to overcome, maintaining good management practices will give better output. Out of the 114 literature selected for this study, only 8 research papers were discussed about the drawbacks and the limitations of the BIV systems which is still having paucity of information.
Keywords: Building Integrated Vegetation systems, Economic Sustainability, Environmental Sustainability, Social Sustainability



